
Cracking the case of the Krakatoa volcano collapse
Scientists this week are on expedition around the volcano Anak Krakatoa, which erupted and collapsed in 2018 leading to the loss of some 400 lives on the island of Java. The scientists, including David Tappin and Michael Cassidy, are hoping that their survey of the seafloor and tsunami debris will allow them to piece together the sequence of events, and maybe find signs to look out for in the future.Wyoming Dinosaur trove The BBC got a secret visit to a newly discovered fossil site somewhere in the US which scientists reckon could keep them busy for many years. Jon Amos got to have a tour and even found out a tasty technique to tell a fossil from a rock.Bioflourescent Aliens Researchers at Cornell University’s Carla Sagan Institute report their work thinking about detecting alien life on distant planets orbiting other stars. Around 75% of stars are of a type that emits far more dangerous UV than our own sun. What, they argue, would a type of life that could survive that look like to us? Well, just maybe it would act like some of our own terrestrial corals, who can protect their symbiotic algae from UV, and in doing so, emit visible light. Could such an emission be detectable, in sync with dangerous emergent UV flares around distant suns? The next generation of large telescopes maybe could…Exopants Jinsoo Kim and David Perry of Harvard University tell reporter Giulia Barbareschi about their new design for a soft exosuit that helps users to walk and, crucially also to run. They suggest the metabolic savings the suit could offer have numerous future applications for work and play.Listeners Mark and Jess have been watching TV series, The Handmaid’s Tale. It's an adaptation of a book by Margaret Atwood and depicts a dystopian future where many have become infertile. The remaining few fertile women, known as Handmaids, are forced into child-bearing servitude. Why so many have become infertile isn’t clear but the series hints at several possible causes, from radiation to environmental pollutants.All of which got Mark and Jess wondering… What could cause mass infertility? Would we descend into a political landscape akin to Gilead? Award-winning author Margaret Atwood has left a paper trail for us to follow in the pages of her novel. There’s a ream of possible causes, and so Marnie Chesterton investigates which ring true.(Photo: Volcano Anak Krakatoa. Credit: Drone Pilot, Muhammad Edo Marshal, ITB university in Bandung, Indonesia)
18 Aug 20191h 13min
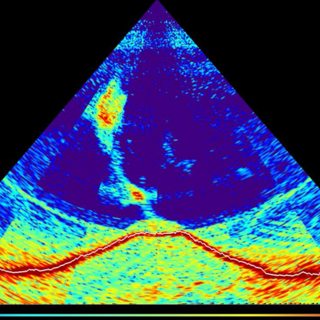
The birth of a new volcano
A new undersea volcano has appeared off the coast of East Africa. The sea floor between Madagascar and Mozambique has become increasingly seismically active in the last year. As well as the appearance of this active volcano, local islands are now experiencing frequent earthquakes. The causes of Indonesia’s Palu Bay tsunami last year are being examined thanks to social media. Videos taken as the tsunami hit have been analysed to determine wave heights and speeds and suggest possible causes. Scientists at a massive underground physics research facility in Italy are to stand trial over safety risks. The facility uses poisonous chemicals. There are concerns these could leak into drinking water supplies in the event of an earthquake. As scientists keep finding ever more fascinating facts about the invisible housemates that share our homes, we investigate what might be lurking in quiet household corners or under our beds. We head out on a microbial safari with expert tour guide Dr Jamie Lorimer from the University of Oxford to find out what kind of creatures are living in our kitchens, bathrooms and gardens - from bacteria normally found in undersea vents popping up in a kettle, to microbes quietly producing tiny nuggets of gold. For so long this hidden world has been one that we’ve routinely exterminated - but should we be exploring it too?(Image: Multibeam sonar waves, reflecting off the sea floor near the French island of Mayotte, reveal the outline of an 800-meter-tall volcano (red) and a rising gas-rich plume. Credit: MAYOBS team (CNRS / IPGP -Université de Paris / Ifremer / BRGM)
26 Maj 20191h 3min




















